Salt (sodium chloride) is one of the most widely used seasonings in the world, but too much of it can turn into a silent killer. While sodium is vital for nerve function, muscle contractions, and fluid balance, excessive intake puts immense pressure on almost every system in your body.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends less than 5 grams (about one teaspoon) per day, but most people consume two to three times this amount through processed foods, snacks, and restaurant meals. Over time, this excess salt can lead to life-threatening health problems.
Let’s explore 7 major dangers of high salt intake and how it can kill you slowly.
1. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
-
How it happens: Salt makes the body retain water, which increases blood volume. This puts extra strain on arteries.
-
Effects: Persistent high blood pressure damages blood vessels, the heart, and kidneys.
-
Long-term risks: Stroke, aneurysm, heart attack.
-
Tip: Replace salty snacks with fruits, veggies, or nuts.
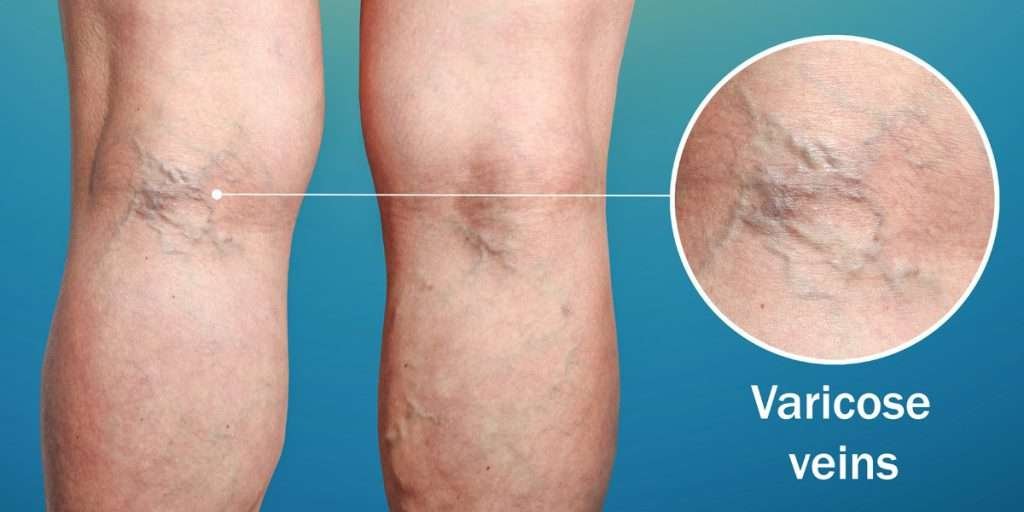
2. Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
-
Impact on the heart: High salt stiffens arteries and increases plaque buildup, forcing the heart to pump harder.
-
Diseases linked to salt:
-
Coronary artery disease
-
Heart failure
-
Enlarged heart muscle (leading to sudden cardiac death)
-
-
Fact: Studies show reducing salt intake lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease by up to 20–30%.
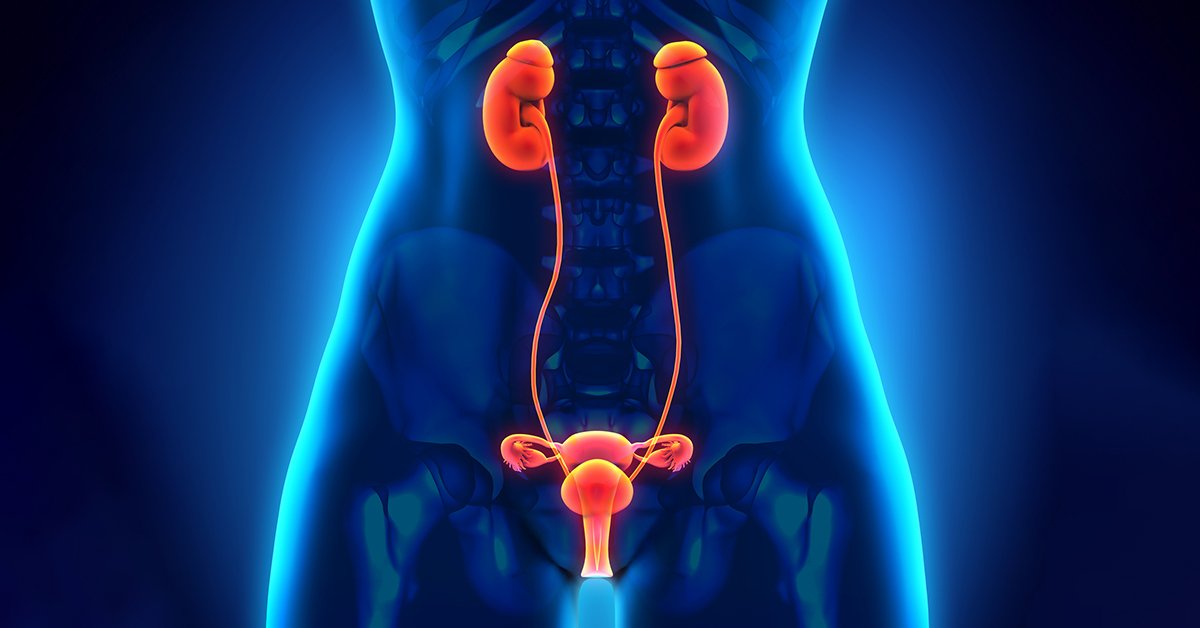
3. Kidney Damage
-
Why kidneys suffer: Kidneys filter sodium from blood. Excess salt overloads them, reducing their efficiency.
-
Complications:
-
Kidney stones (calcium builds up in urine)
-
Chronic kidney disease
-
End-stage renal failure (dialysis needed)
-
-
Warning sign: Swelling in feet/ankles often signals poor kidney function linked to salt.
4. Water Retention & Bloating
-
Short-term effect: Eating salty foods (like chips, fast food, pickles) makes your body hold water.
-
Symptoms: Puffy face, swollen hands/feet, bloating in the stomach.
-
Long-term danger: Fluid retention puts stress on the heart and lungs, sometimes leading to pulmonary edema (fluid in lungs).
5. Osteoporosis (Weak & Brittle Bones)
-
How salt harms bones: High sodium levels cause calcium loss through urine.
-
Result: Bones become weaker over time.
-
Who is at risk: Post-menopausal women and elderly people.
-
Fact: Every extra 1 gram of salt eaten daily causes the body to lose 40 mg of calcium.
6. Stomach Cancer
-
How salt causes damage:
-
Irritates the stomach lining
-
Encourages H. pylori bacteria growth (a major cause of ulcers and cancer)
-
-
Studies show: People with high-salt diets are 68% more likely to develop stomach cancer.
-
Prevention tip: Cut down on processed meats, pickled foods, and instant noodles.
7. Impaired Cognitive Function (Brain Damage)
-
Salt’s effect on the brain: Too much sodium reduces blood flow to brain tissues.
-
Consequences:
-
Memory loss
-
Difficulty concentrating
-
Higher risk of dementia & Alzheimer’s disease
-
-
Study: A diet high in salt combined with low physical activity was linked to faster cognitive decline in older adults.
Bonus: Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalance
-
Sodium works with potassium to maintain balance in the body.
-
Too much salt throws off this balance, leading to:
-
Fatigue
-
Headaches
-
Muscle cramps
-
Severe dehydration risk
-
How Much Salt Is Safe?
-
WHO guideline: Less than 5 grams (1 teaspoon) daily.
-
American Heart Association: Ideally less than 2.3 grams of sodium per day.
-
Hidden salt sources: Bread, cheese, sauces, chips, canned food, and fast food.
How to Reduce Salt Intake
-
Read nutrition labels and choose “low-sodium” options.
-
Cook at home and flavor meals with herbs, lemon, or spices instead of salt.
-
Limit processed and packaged foods.
-
Rinse canned beans/vegetables before eating.
-
Gradually cut down to allow your taste buds to adjust.
Conclusion
Salt may seem harmless, but too much can quietly destroy your health—damaging your heart, kidneys, bones, brain, and even increasing cancer risk. The good news? Small lifestyle changes like cooking fresh meals, checking food labels, and reducing processed foods can drastically lower your sodium intake and extend your life.